nLab nodal curve
Context
Elliptic cohomology
Geometry
higher geometry / derived geometry
Ingredients
Concepts
-
geometric little (∞,1)-toposes
-
geometric big (∞,1)-toposes
Constructions
Examples
-
derived smooth geometry
Theorems
Contents
Idea
A nodal singularity of an algebraic curve is one of the form parameterized by the equation . A nodal curve is a curve with a nodal singularity.
(e.g. Hain 08, p. 45)
The nodal cubic
The nodal cubic curve (over some base) is (see at elliptic curve – Nodal curves and cuspidal curves for notation and background) the solution to the Weierstrass equation for which the discriminant vanishes, but the modular invariant does not.
This is equivalently the limit in which the j-invariant goes to .
Properties of the nodal cubic
Compactified moduli stack of elliptic curves and the Tate curve
The nodal cubic curve is not an elliptic curve, as it is singular, but adding it to the moduli stack of elliptic curves produces the compactification which is often relevant.
The formal neighbourhood of the nodal curve in is the Tate curve.
Over the complex numbers
Over the complex numbers, the nodal cubic is the Riemann sphere/complex projective space with the pole points 0 and identified (hence is a “complex torus with one cycle shrunk away”). Precisely: there is a holomorphic function
which is onto , sends the unit of the multiplicative group to the unit of , maps both to the nodal singular double point of and is injective away from these points (e.g. Hain 08, exercise 47, p. 45)
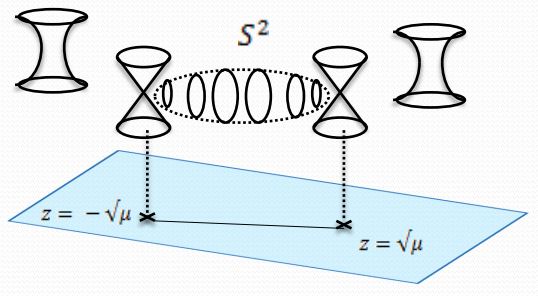
Formal group and height
The formal group associated with a nodal cubic curve is of height 1. Indeed, passing to the point of the nodal curve in connects elliptic cohomology (of chromatic level 2) to topological K-theory (of chromatic level 1). For more on this see at moduli stack of tori and at tmf – Properties – Maps to K-theory and to Tate K-theory.
Relation to gauge enhancement in F-theory
In F-theory the nodal singularity locus of the given elliptic fibration is interpreted as the locus of D7-branes, see at F-brane scan.
Related concepts
-
in F-theory the points where the fibers of the elliptic fibration degenerate to the nodal curve are where the D7-branes are located
References
Discussion over the complex numbers is in
- Richard Hain, section 5.2 of Lectures on Moduli Spaces of Elliptic Curves (arXiv:0812.1803)
Last revised on December 21, 2020 at 12:17:04. See the history of this page for a list of all contributions to it.