nLab stringy weight system
Context
Knot theory
Examples/classes:
Types
Related concepts:
Contents
Idea
Where a weight system on chord diagrams is equivalently a weight system on Jacobi diagrams (since chord diagrams modulo 4T are Jacobi diagrams modulo STU) and hence an assignment of Feynman amplitude-factors to Chern-Simons-Feynman diagrams (in the presence of a Wilson loop), a stringy weight system assigns such amplitude factors instead to the ribbon graph surfaces of open string worldsheets which become Jacobi diagrams in the point particle limit (Bar-Natan 95, Theorem 10, see also Kneissler 97, Section 1.3)
Details
Given any ground field , consider
the linear span of the set of diffeomorphism classes of surfaces with boundary equipped with a finite number of chosen oriented points on their boundary, at least one on each connected component (Bar-Natan 95, Def. 1.12).
A stringy weight system is a linear map from this space to the ground field, hence the space of stringy weight systems is the dual vector space
Of course a linear function is equivalently a plain function , but for the following construction it is necessary to consider formal linear combinations of marked surfaces:
The 't Hooft double line construction constitutes a linear map from the linear span of Jacobi diagrams modulo STU-relations to the linear span of marked surfaces (1)
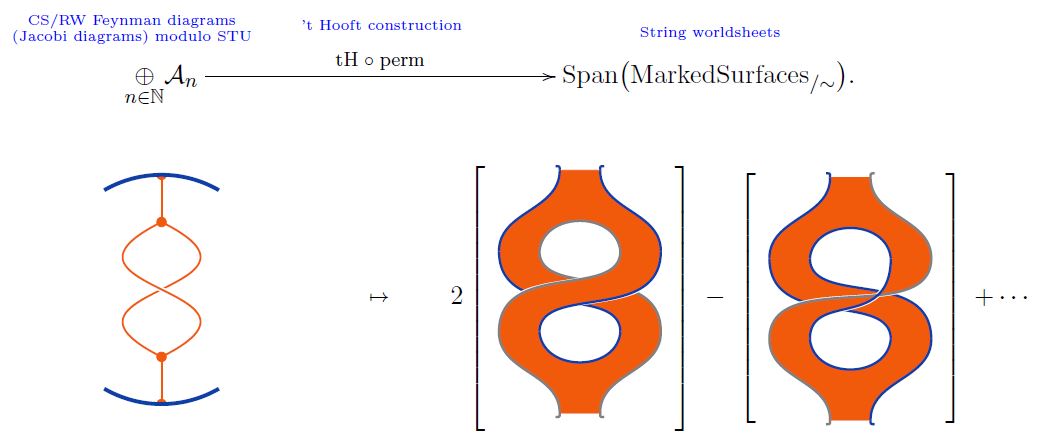
(Bar-Natan 95, Theorem 10 with Theorem 8)
graphics from Sati-Schreiber 19c
Under passage to dual vector spaces this yields a linear map
from stringy weight systems (2) to ordinary weight systems. This may be regarded as the point particle limit of stringy weight systems.
Properties
Relation to Lie algebra weight systems
Remark
(stringy weight systems span classical Lie algebra weight systems)
The image of the vector space (2) of stringy weight systems under the point particle limit map (3) inside the space of ordinary weight systems coincides with the direct sum of the linear span of Lie algebra weight systems for the general linear Lie algebras and the special orthogonal Lie algebras , and contains that of symplectic Lie algebras :
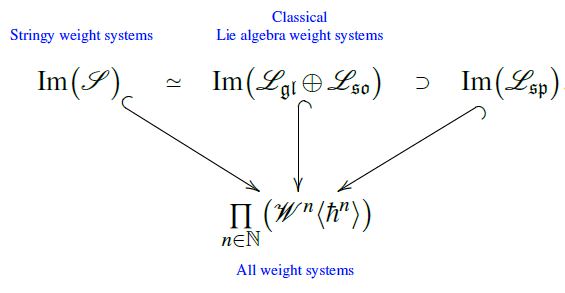
graphics from Sati-Schreiber 19c
Related concepts
| chord diagrams | weight systems |
|---|---|
| linear chord diagrams, round chord diagrams Jacobi diagrams, Sullivan chord diagrams | Lie algebra weight systems, stringy weight system, Rozansky-Witten weight systems |
References
The concept (not by this name, though) is due to
- Dror Bar-Natan, p. 9 and section 6 of: On the Vassiliev knot invariants, Topology Volume 34, Issue 2, April 1995, Pages 423-472 (doi:10.1016/0040-9383(95)93237-2, pdf)
where it is attributed (Remark 1.13) to private communication with Maxim Kontsevich.
See also
-
Jan Kneissler, Section 1.3 of: The number of primitive Vassiliev invariants up to degree 12 (arXiv:q-alg/9706022)
-
Sergei Chmutov, Sergei Duzhin, Jacob Mostovoy, Section 6.2.4 of: Introduction to Vassiliev knot invariants, Cambridge University Press, 2012 (arxiv:1103.5628, doi:10.1017/CBO9781139107846)
Last revised on January 9, 2020 at 09:06:37. See the history of this page for a list of all contributions to it.