nLab f1-meson
Context
Fields and quanta
fields and particles in particle physics
and in the standard model of particle physics:
matter field fermions (spinors, Dirac fields)
| flavors of fundamental fermions in the standard model of particle physics: | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| generation of fermions | 1st generation | 2nd generation | 3d generation |
| quarks () | |||
| up-type | up quark () | charm quark () | top quark () |
| down-type | down quark () | strange quark () | bottom quark () |
| leptons | |||
| charged | electron | muon | tauon |
| neutral | electron neutrino | muon neutrino | tau neutrino |
| bound states: | |||
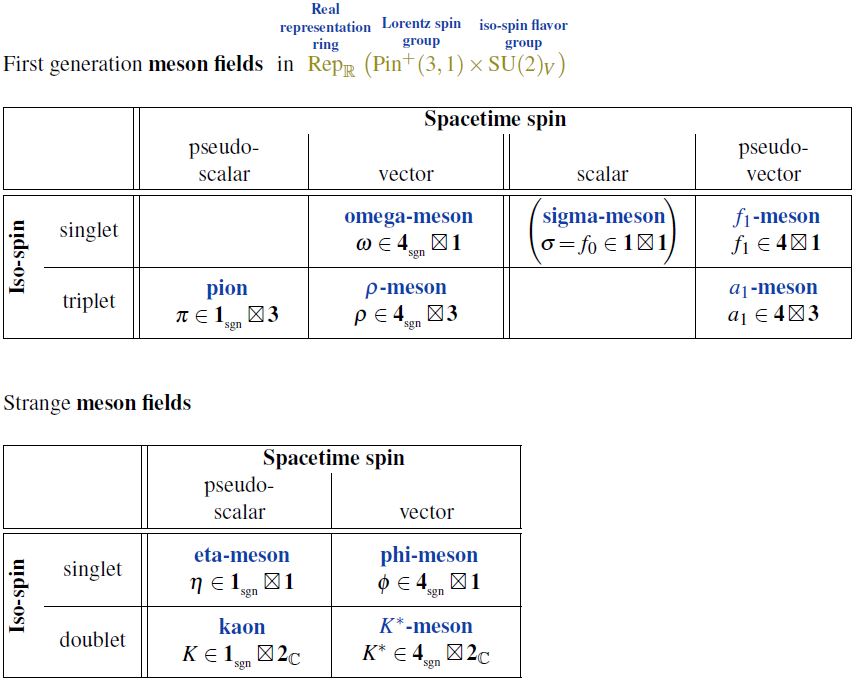
| mesons | light mesons: pion () ρ-meson () ω-meson () f1-meson a1-meson | strange-mesons: ϕ-meson (), kaon, K*-meson (, ) eta-meson () charmed heavy mesons: D-meson (, , ) J/ψ-meson () | bottom heavy mesons: B-meson () ϒ-meson () |
| baryons | nucleons: proton neutron |
(also: antiparticles)
hadrons (bound states of the above quarks)
minimally extended supersymmetric standard model
bosinos:
dark matter candidates
Exotica
Contents
Idea
The -meson is the light meson which (in the Wigner classification) is the Lorentz spin group pseudo-vector representation and isospin scalar.
This is the chiral partner of the omega-meson.
References
-
Su Houng Lee, Observing chiral partners in nuclear medium (pdf)
-
M. Kirchbach, D. O. Riska, The Coupling of the meson to the isoscalar axial current of the nucleon, Nucl. Phys.A 594 (1995) 419-424 (arXiv:nucl-th/9502018)
-
Robert Pisarski, p. 1 of: Where does the Rho Go? Chirally Symmetric Vector Mesons in the Quark-Gluon Plasma, Phys. Rev. D52 (1995) 3773-3776 (arXiv:hep-ph/9503328)
-
A. E. Dorokhova, N. I. Kochelevba. A. P. Martynenkoc. F. A. Martynenkoc. A. E. Radzhabovb, The contribution of axial-vector mesons to hyperfine structure of muonic hydrogen, Physics Letters B Volume 776, 10 January 2018, Pages 105-110 Physics Letters B (doi:10.1016/j.physletb.2017.11.027)
Last revised on May 4, 2020 at 19:45:33. See the history of this page for a list of all contributions to it.