nLab non-abelian de Rham cohomology
Context
Cohomology
Special and general types
-
group cohomology, nonabelian group cohomology, Lie group cohomology
-
-
cohomology with constant coefficients / with a local system of coefficients
Special notions
Variants
-
differential cohomology
Extra structure
Operations
Theorems
Differential geometry
synthetic differential geometry
Introductions
from point-set topology to differentiable manifolds
geometry of physics: coordinate systems, smooth spaces, manifolds, smooth homotopy types, supergeometry
Differentials
Tangency
The magic algebraic facts
Theorems
Axiomatics
Models
differential equations, variational calculus
Chern-Weil theory, ∞-Chern-Weil theory
Cartan geometry (super, higher)
Contents
Idea
For a smooth manifold, the traditional coboundary-relation which defines the ordinary de Rham cohomology-classes of closed differential n-forms
is equivalent to the concordance-relation [FSS20, Prop. 6.4]
But the latter concordance-relation immediately generalizes to flat -algebra valued differential forms
with coefficients in any -algebra , which reduces to the ordinary case for the line Lie -algebra.
Therefore it makes sense to define [FSS20, Def. 6.3]:
Definition
The non-abelian de Rham cohomology of a smooth manifold with coefficients in a -algebra is the set of concordance classes of flat -valued differential forms on :
Examples
Example
With (1) it follows that the ordinary de Rham cohomology in degree is equivalently non-abelian de Rham cohomology with coefficients in the line Lie n-algebra :
Example
In higher gauge theories of Maxwell-type, nonabelian de Rham cohomology of a Cauchy surface with coefficients in an L-infinity algebra characteristic of the theory’s Gauss law reflects the total flux of the higher gauge fields.
See at geometry of physics – flux quantization the section Total flux in Nonabelian de Rham cohomology.
Properties
Recipient of non-abelian character map
For (the homotopy type of) a topological space which is nilpotent (for instance: simply connected) and of rational finite type (all its rational cohomology-groups are finite-dimensional -vector spaces) one may regard the homotopy classes of maps into as the nonabelian cohomology classified by (the non-abelian cohomology in degree=1 with coefficients in the loop space -group ):
For example, in the case that
is an Eilenberg-MacLane space for a discrete abelian group , this reduces to ordinary cohomology:
or if
is the classifying space KU for complex topological K-theory, then this reduces to to complex topological K-theory:
Generally, if is an Omega-spectrum of spaces, then
coincides with the Whitehead-generalized -cohomology.
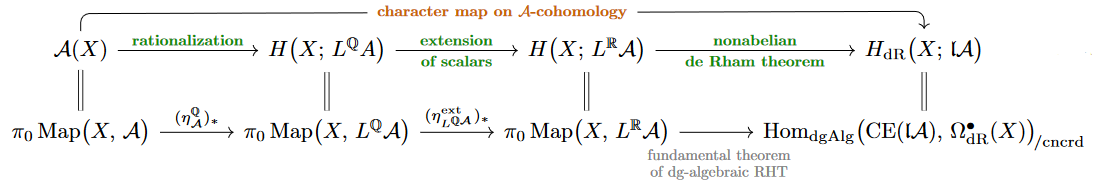
Now the rationalization-unit followed by suitable extension of scalars along induces cohomology operations in the non-abelian cohomology (3), to what may be called non-abelian rational cohomology, and non-abelian real cohomology with coefficients in
and, shown on the right, a non-abelian version of the de Rham theorem — given essentially by the fundamental theorem of dg-algebraic rational homotopy theory — identifies this non-abelian real cohomology with coefficients in with the non-abelian de Rham cohomology (2) with coefficients in the real-Whitehead -algebra of .
For the case that the cohomology operation (4) coincides with the Chern character on complex topological K-theory, and generally for a term in an Omega-spectrum it coincides with the Chern-Dold character map on Whitehead-generalized cohomology (Prop. 7.2).
Therefore, it makes sense to refer to (4) generally as the character map on nonabelian cohomology taking values in non-abelian de Rham cohomology (FSS20, Part IV).
Related entries
References
- Domenico Fiorenza, Hisham Sati, Urs Schreiber, Part III of: The Character Map in Nonabelian Cohomology — Twisted, Differential, Generalized, World Scientific (2023) [arXiv:2009.11909, doi:10.1142/13422]
Last revised on January 30, 2024 at 12:17:59. See the history of this page for a list of all contributions to it.