nLab Hadamard gate
Context
Quantum systems
-
quantum algorithms:
Constructivism, Realizability, Computability
constructive mathematics, realizability, computability
propositions as types, proofs as programs, computational trinitarianism
Constructive mathematics
Realizability
Computability
Contents
Idea
In quantum computing/quantum information theory, by the Hadamard gate one means the quantum logic gate which acts on a single qbit by
hence which is the linear map which in the standard linear basis is given by the matrix
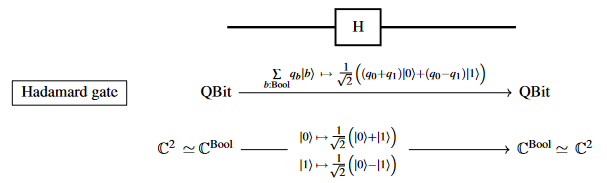
Simple as it is, the Hadamard gate plays a central role in theory and practice of quantum circuits, notably where in its combination with the CNOT gate it is used to produce Bell states (such as in the quantum teleportation protocol).
Related gates
References
-
Emanuel Knill, p. 10 in: Conventions for quantum pseudocode Los Alamos Technical Report (1996) LA-UR-96-2724, doi:10.2172/366453, pdf, pdf
-
Michael A. Nielsen, Isaac L. Chuang, p. 28 in: Quantum computation and quantum information, Cambridge University Press (2000) doi:10.1017/CBO9780511976667, pdf, pdf
See also:
- Wikipedia, Quantum logic – Hadamard gate
Last revised on February 8, 2025 at 09:11:21. See the history of this page for a list of all contributions to it.