nLab bit flip code
Context
Quantum systems
-
quantum algorithms:
Computation
constructive mathematics, realizability, computability
propositions as types, proofs as programs, computational trinitarianism
Constructive mathematics
Realizability
Computability
Contents
Idea
In quantum information theory a bit flip code is a quantum error correcting code to correct for quantum noise caused by bit flip channels.
Details
3-qbit flip code
The following basic example of a bit flip code encodes single logical qbits in triples of physical qbits.
Idea
Here the Hilbert space
of a single logical qbit has complex dimension . Inside this is the space of undisturbed logical qbits
as well as three further orthogonal subspaces which are the images of this one under one of the three single bit flips, respectively:
The 4 labels of these three subspaces are called the “error syndrome”, which we collect in the 4-element set
to express the logical q-bit space alternatively in this linear basis:
Remark
Beware that there is no room to record the further possible errors of 2 qbits flipping at once. Instead, this error process takes pure qbits to one of the subspaces reserved for single bit flips. Similarly, if all three bits flip at once, the initial pure state remains in the subspace reserved for pure states, but now with its phases mixed up. Therefore, the following error correction code fails on flips of more than one of the 3-qbits and will reduce the overall error probability only if single bit flips are sufficiently more likely than double and triple spin flips.
The error correction now proceeds by:
-
Performing a quantum measurement of the above error syndrome on the logical Qbit space. While this measurement collapses the quantum state onto the subspace the particular logical qbit states of the pure form (1) lose no information under this collapse, in that there is a unitary operator on which turns any such collapse state back into the original qbit state.
-
applying this correcting unitary , which is evidently the “Pauli X-” (or “NOT-”)quantum gate acting on the -th qbit:
-
re-preparing a logical QBit from the recovered Qbit.
Circuit diagram and pseudo-code
In terms of quantum circuit diagrams and the QS-pseudo-code, the 3-bit flip error correcting code looks as follows (following the notation from quantum circuits via dependent linear types):
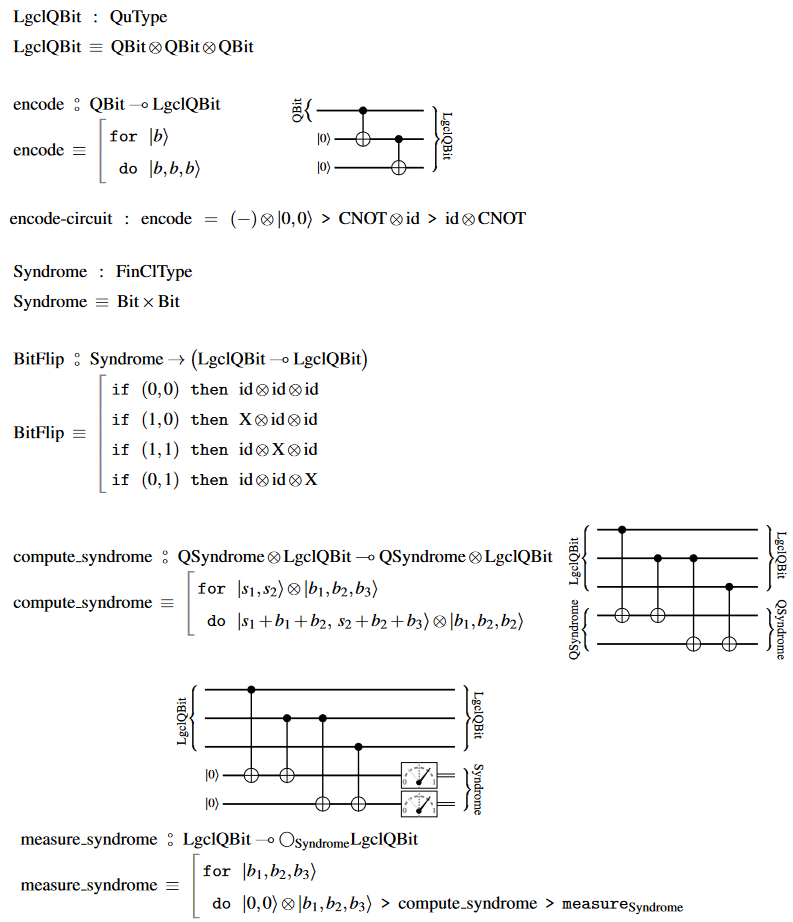
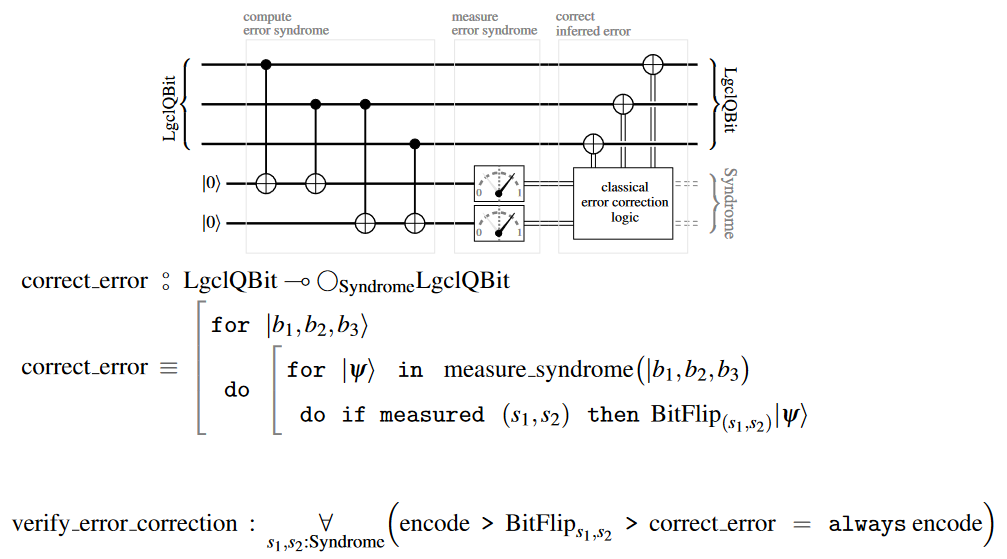
Related concepts
References
-
Michael A. Nielsen, Isaac L. Chuang, §10.1.1 in: Quantum computation and quantum information, Cambridge University Press (2000) [doi:10.1017/CBO9780511976667, pdf, pdf]
-
Simon J. Devitt, Kae Nemoto, William J. Munro, §IV of: Quantum Error Correction for Beginners, Rep. Prog. Phys. 76 (2013) 076001 [arXiv:0905.2794, doi:10.1088/0034-4885/76/7/076001]
Last revised on November 23, 2023 at 20:10:46. See the history of this page for a list of all contributions to it.