nLab GUT
Context
Fields and quanta
fields and particles in particle physics
and in the standard model of particle physics:
matter field fermions (spinors, Dirac fields)
| flavors of fundamental fermions in the standard model of particle physics: | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| generation of fermions | 1st generation | 2nd generation | 3d generation |
| quarks () | |||
| up-type | up quark () | charm quark () | top quark () |
| down-type | down quark () | strange quark () | bottom quark () |
| leptons | |||
| charged | electron | muon | tauon |
| neutral | electron neutrino | muon neutrino | tau neutrino |
| bound states: | |||
| mesons | light mesons: pion () ρ-meson () ω-meson () f1-meson a1-meson | strange-mesons: ϕ-meson (), kaon, K*-meson (, ) eta-meson () charmed heavy mesons: D-meson (, , ) J/ψ-meson () | bottom heavy mesons: B-meson () ϒ-meson () |
| baryons | nucleons: proton neutron |
(also: antiparticles)
hadrons (bound states of the above quarks)
minimally extended supersymmetric standard model
bosinos:
dark matter candidates
Exotica
Contents
Idea
General idea
The standard model of particle physics asserts that the fundamental quantum physical fields and particles are modeled as sections of and connections on a vector bundle that is associated to a -principal bundle, where the Lie group – called the gauge group – is the product of (special) unitary groups (or rather a quotient of this by the cyclic group , see there) and where the representation of used to form the associated vector bundle looks fairly ad hoc on first sight.
A grand unified theory (“GUT” for short) in this context is an attempt to realize the standard model as sitting inside a conceptually simpler model, in particular one for which the gauge group is a bigger but simpler group , preferably a simple Lie group in the technical sense, which contains as a subgroup. Such a grand unified theory would be phenomenologically viable if a process of spontaneous symmetry breaking at some high energy scale – the “GUT scale” – would reduce the model back to the standard model of particle physics without adding spurious extra effects that would not be in agreement with existing observations in experiment.
The terminology “grand unified” here refers to the fact that such a single simple group would unify the fundamental forces of electromagnetism, the weak nuclear force and the strong nuclear force in a way that generalizes the way in which the electroweak field already unifies the weak nuclear force and electromagnetism, and electromagnetism already unifies, as the word says, electricity and magnetism.
Since no GUT model has been fully validated yet (but see for instance Fong-Meloni 14), GUTs are models “beyond the standard model”. Often quantum physics “beyond the standard model” is expected to also say something sensible about quantum gravity and hence unify not just the three gauge forces but also the fourth known fundamental force, which is gravity. Models that aim to do all of this would then “unify” the entire content of the standard model of particle physics plus the standard model of cosmology, hence “everything that is known about fundamental physics” to date. Therefore such theories are then sometimes called a theory of everything.
(Here it is important to remember the context, both “grand unified” and “of everything” refers to aspects of presently available models of fundamental physics, and not to deeper philosophical questions of ontology.)
length scales in the observable universe (from cosmic scales, over fundamental particle-masses around the electroweak symmetry breaking to GUT scale and Planck scale):
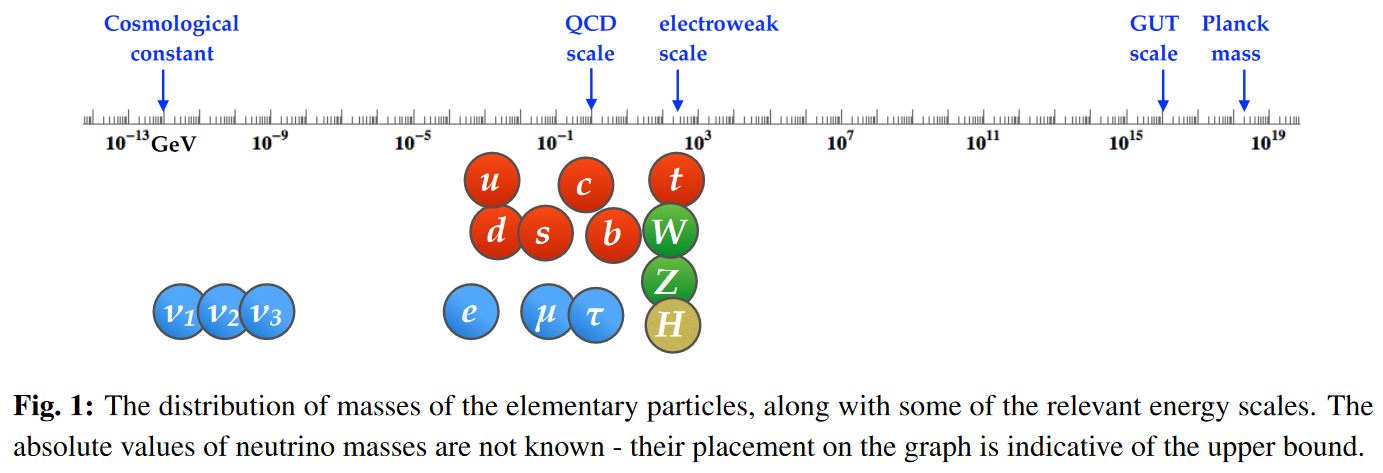
graphics grabbed from Zupan 19
The -GUT (Georgi-Glashow)
The argument for the hypothesis of “grand unification” is fairly compelling if one asks for simple algebraic structures in the technical sense (simple Lie groups and their irreducible representations):
The exact gauge group of the standard model of particle physics is really a quotient group
where the cyclic group acts freely, hence exhibiting a subtle global twist in the gauge structure. This seemingly ad hoc group turns out to be isomorphic to the subgroup
of SU(5) (see Baez-Huerta 09, p. 33-36). The latter happens to be a simple Lie group, thus exhibiting the exact standard model Lie group as being “simply” a “(2+3)-breaking” of a simple Lie group.
Moreover, the gauge group-representation that captures one generation of fundamental particles of the standard model of particle physics, which looks fairly ad hoc as a representation of (e.g. Baez-Huerta 09, table 1), but as a representation of it is simply
(see Baez-Huerta 09, p. 36-41).
This leads to the -GUT due to Georgi-Glashow 74
D-Series GUTs
The -GUT (known as “”)
There is a further inclusion Spin(10) into the spin group in 10 (Euclidean) dimensions (still a simple Lie group), and one generation of fundamental particles regarded as an -representation as above extends to a spin representation (see Baez-Huerta 09, theorem 2). This has the aesthetically pleasing effect that under this identification the 1-generation rep is now identified as
namely as the direct sum of the two (complex) irreducible representations of Spin(10), together being the Dirac representation of Spin(10).
The exact gauge group of the standard model of particle physics (see there) is isomorphic to the subgroup of Spin(9) Spin(10) which respects a splitting (Krasnov 19).
Again, this means that under the embedding of the gauge group all the way into the simple Lie group Spin(10), its ingredients become simpler, not just in a naive sense, but in the technical mathematical sense of simple algebraic objects.
Discussion of SO(10) (i.e. Spin(10)) GUT-models with realistic phenomenology is in BLM 09 Malinský 09, Lavoura-Wolfenstein 10 Altarelli-Meloni 13 Dueck-Rodejohann 13 Ohlsson-Pernow 19 CPS 19.
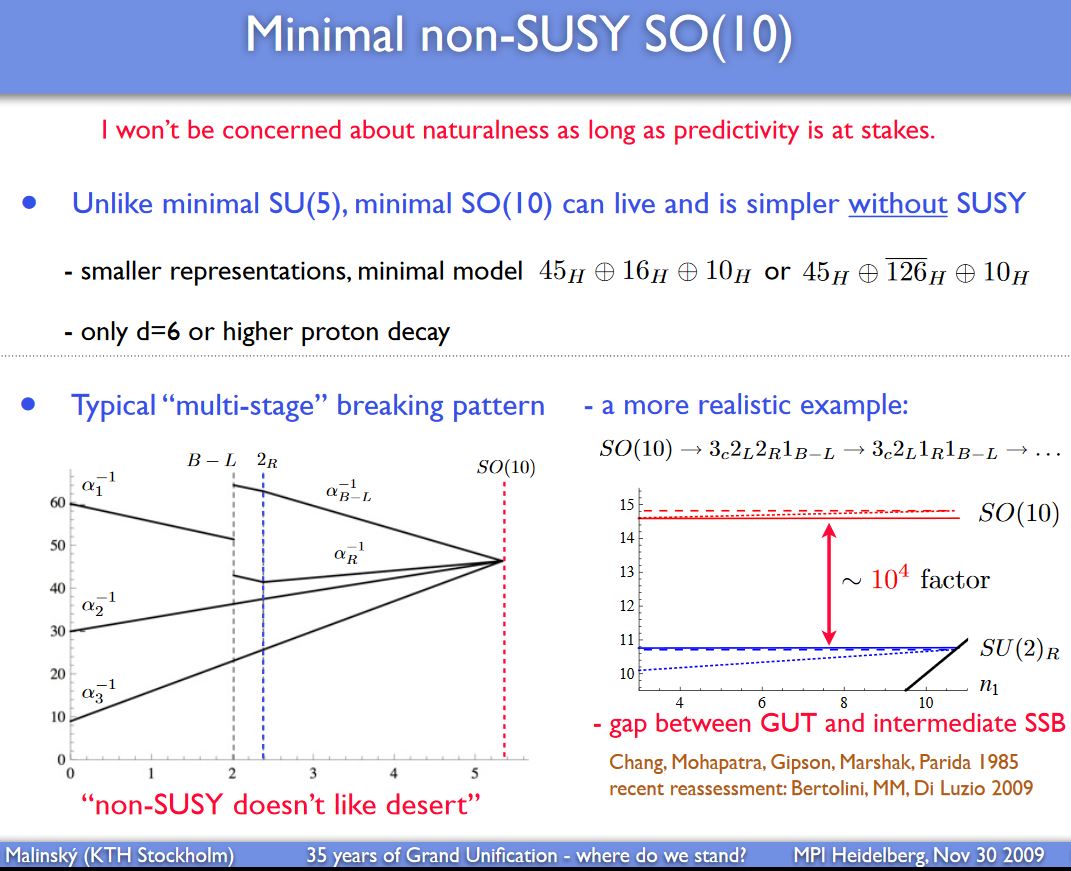
slide grabbed from Malinský 09
Discussion of leptoquarks in -models possibly explaining the flavour anomalies: AMM 19
The -GUT (known as “”)
Models with Spin(11) (“SO(11)”) GUT group.
Specifically with gauge-Higgs unification in a Randall-Sundrum model-like 6d spacetime: Hosotani-Yamatsu 15, Furui-Hosotani-Yamatsu 16, Hosotani 17, Hosotani-Yamatsu 17
See the references below.
The -GUT (known as “”)
Models with Spin(12) (“SO(12)”) GUT group.
Specifically with gauge-Higgs unification in a Randall-Sundrum model-like 6d spacetime: Nomura-Sato 08, Nomura 09, Chiang-Nomura-Sato 11)
See the references below.
The -GUT (known as “”)
Models with Spin(16) (“SO(16)”) GUT group.
Wilczek-Zee 82, Senjanovic-Wilczek-Zee 84, Martínez-Melfo-Nesti-Senjanovic 11
See also di Lucio 11, p. 44 and see the references below.
Predicts fourth generation of fermions…
E-series GUTs
The most studied choices of GUT-groups are SU(5), Spin(10) (in the physics literature often referred to as SO(10)) and E6 (review includes Witten 86, sections 1 and 2).
It so happens that, mathematically, the sequence SU(5), Spin(10), E6 naturally continues (each step by consecutively adding a node to the Dynkin diagrams) with the exceptional Lie groups E7, E8 that naturally appear in heterotic string phenomenology (exposition is in Witten 02a) and conjecturally further via the U-duality Kac-Moody groups E9, E10, E11 that are being argued to underly M-theory. In the context of F-theory model building, also properties of the observes Yukawa couplings may point to exceptional GUT groups (Zoccarato 14, slide 11, Vafa 15, slide 11).
The -GUT
(…)
review in Britto 17
(…)
The -GUT (?)
(…)
The -GUT (?)
(…)
Properties
Relation to proton decay
Many GUT models imply that the proton – which in the standard model of particle physics is a stable bound state (of quarks) – is in fact unstable, albeit with an extremely long mean liftetime, and hence may decay (e.g. KM 14). Experimental searches for such proton decay (see there for more) put strong bounds on this effect and hence heavily constrain or rule out many GUT models.
But in recent years it is claimed that there are in fact realistic GUT models that do not imply any proton decay, quite generically so for MSSM-models (Mütter-Ratz-Vaudrvange 16), but also for non-supersymmetric models ( Fornal-Grinstein 17, Fornal-Grinstein 18, in particular in gauge-Higgs grand unification such as Spin(11)- (“SO(11)”-) and Spin(12)- (“SO(12)”-) models: (Hosotani-Yamatsu 15, Furui-Hosotani-Yamatsu 16, Sec. 2.6 Hosotani 17, Section 6).
Relation to neutrino masses
The high energy scale required by a seesaw mechanism to produce the experimentally observer neutrino masses happens to be about the conventional GUT scale, for review see for instance (Mohapatra 06).
I also noted at the same time that interactions between a pair of lepton doublets and a pair of scalar doublets can generate a neutrino mass, which is suppressed only by a factor , and that therefore with a reasonable estimate of could produce observable neutrino oscillations. The subsequent confirmation of neutrino oscillations lends support to the view of the Standard Model as an effective field theory, with M somewhere in the neighborhood of . (Weinberg 09, p. 15)
Detailed matching of parameters of non-supersymmetric -GUT to neutrino masses is discussed in Ohlsson-Pernow 19
Relation to leptoquarks
Generically, GUT-theories predict the existence of leptoquarks (Murayama-Yanagida 92), possibly related to the apparently observed
-
flavour anomalies (BDFKFS 18, AMM 19, Heek-Teresi 18, Heek-Teresi 19)
-
anomalies in anomalous magnetic moment of muon and electron
Occurrence in string phenomenology
Discussion of string phenomenology of intersecting D-brane models KK-compactified with non-geometric fibers such that the would-be string sigma-models with these target spaces are in fact Gepner models (in the sense of Spectral Standard Model and String Compactifications) is in (Dijkstra-Huiszoon-Schellekens 04a, Dijkstra-Huiszoon-Schellekens 04b):
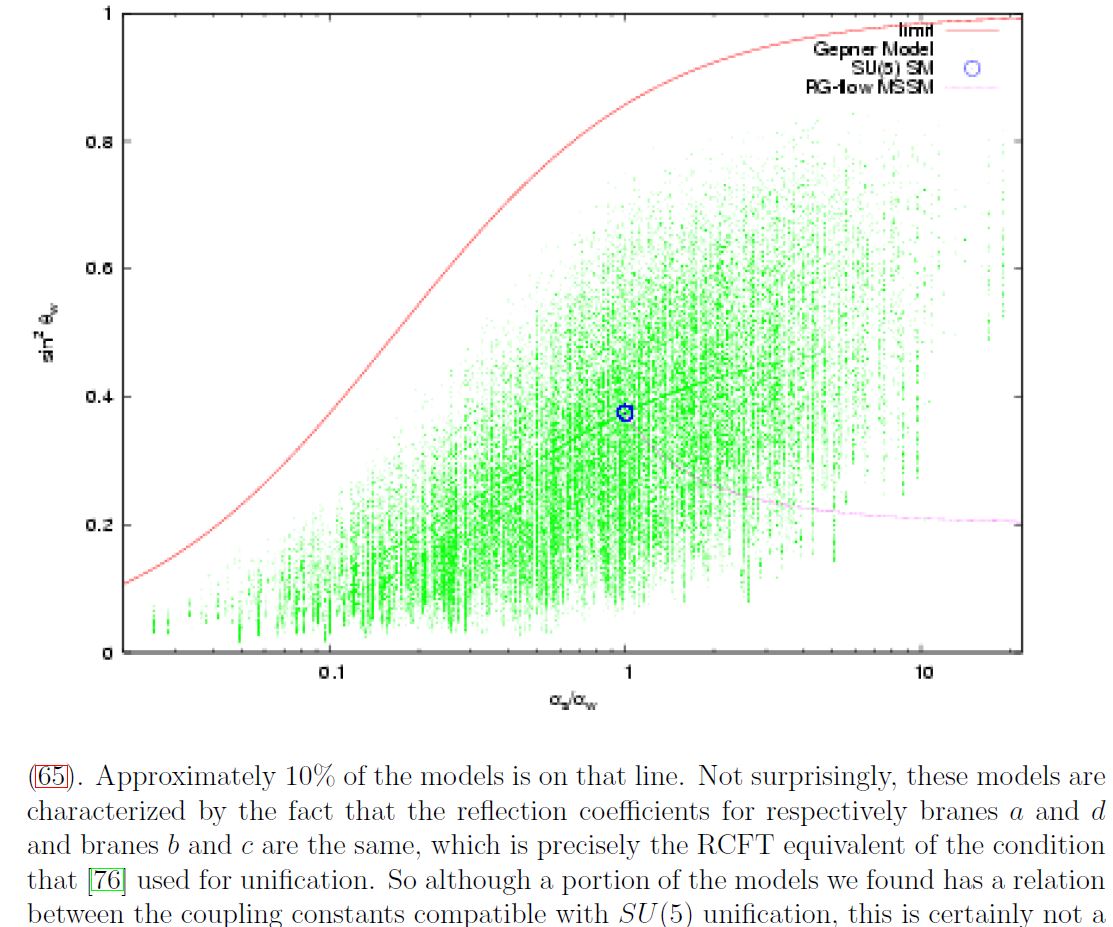
A plot of standard model-like coupling constants in a computer scan of Gepner model-KK-compactification of intersecting D-brane models according to Dijkstra-Huiszoon-Schellekens 04b.
The blue dot indicates the couplings in -GUT theory. The faint lines are NOT drawn by hand, but reflect increased density of Gepner models as seen by the computer scan.
Related concepts
fundamental scales (fundamental/natural physical units)
References
General
Original articles include
-
Jogesh Pati, Abdus Salam, Lepton number as the fourth “color”, Phys. Rev. D 10, 275 – Published 1 July 1974 (doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.10.275)
-
Howard Georgi, Sheldon Glashow, Unity of All Elementary-Particle Forces, Phys. Rev. Lett. 32 (1974) 438 [doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.32.438]
Textbook accounts:
-
Robert E. Marshak, Chapter 8 of: Conceptual Foundations of Modern Particle Physics, World Scientific 1993 (doi:10.1142/1767)
-
Howard Georgi, §18 in: Lie Algebras In Particle Physics, Westview Press (1999), CRC Press (2019) [doi:10.1201/9780429499210]
See also
-
Wikipedia, Pati-Salam model
-
Wikipedia, Grand unification energy
Discussion with an eye towards supergravity unification:
-
Murray Gell-Mann, introductory talk at Shelter Island II, 1983 (pdf)
in: Shelter Island II: Proceedings of the 1983 Shelter Island Conference on Quantum Field Theory and the Fundamental Problems of Physics. MIT Press. pp. 301–343. ISBN 0-262-10031-2.
-
Murray Gell-Mann, Pierre Ramond, Richard Slansky, Complex Spinors and Unified Theories, Supergravity, Peter van Nieuwenhuizen and D.Z. Freedman, eds, North Holland Publishing Co, 1979, (reprinted as arXiv:1306.4669)
A basic textbook account is in
- Luis Ibáñez, Angel Uranga, section 1.2 of String Theory and Particle Physics – An Introduction to String Phenomenology, Cambridge University Press 2012
and a detailed one is in
- A. Hebecker, J. Hisano, Grand Unified Theories, chapter 114. in Particle Data Group’s The Review of Particle Physics 2018 (pdf)
See also:
-
Luca di Lucio: Aspects of Symmetry Breaking inGrand Unified Theories (2011) [pdf]
-
Giacomo Cacciapaglia, Aldo Deandrea, Konstantinos Kollias, Francesco Sannino l: Grand-unification Theory Atlas: Standard Model and Beyond [arXiv:2507.06368]
Survey of arguments for the hypothesis of grand unification includes
-
Michael Peskin, Beyond the Standard Model (arXiv:hep-ph/9705479)
-
Jogesh Pati, Discovery of Proton Decay: A Must for Theory, a Challenge for Experiment (arXiv:hep-ph/0005095)
-
Edward Witten, Quest For Unification, Heinrich Hertz lecture at SUSY 2002 at DESY, Hamburg (arXiv:hep-ph/0207124)
Introductions to GUTs aimed more at mathematicians:
-
Edward Witten, section 1 and 2 of Physics and geometry, Proceedings of the international congress of mathematicians, 1986 (pdf)
-
John Baez, John Huerta, The algebra of grand unified theories, Bull. Am. Math. Soc. 47:483-552,2010 (arXiv:0904.1556)
-
Vivian Anthony Britto, A Mathematical Construction of an Grand Unified Theory, Munich 2017 (pdf, pdf)
On division-algebraic relations in GUT-symmetry breaking:
-
Nichol Furey, An Algebraic Roadmap of Particle Theories, Part I: General construction [arXiv:2312.12377]
-
Nichol Furey, An Algebraic Roadmap of Particle Theories, Part II: Theoretical checkpoints [arXiv:2312.12799]
-
Nichol Furey, An Algebraic Roadmap of Particle Theories, Part III: Intersections [arXiv:2312.14207]
See also
- Mario Fernández Navarro, Stephen F. King, Avelino Vicente, Tri-unification: a separate for each fermion family [arXiv:2311.05683]
Proton (non-)decay
Discussion of experimental bounds on proton decay in GUTs includes
- Helena Kolešová, Michal Malinský, Proton lifetime in the minimal GUT and its implications for the LHC, Phys. Rev. D 90, 115001 (2014) (arXiv:1409.4961)
Claim that proton decay may be entirely avoided:
-
Andreas Mütter, Michael Ratz, Patrick K.S. Vaudrevange, Grand Unification without Proton Decay (arXiv:1606.02303)
(claims that many string theory and supergravity models have this property)
-
Bartosz Fornal, Benjamin Grinstein, Unification without Proton Decay, Physics Review Letters (arXiv:1706.08535)
-
Bartosz Fornal, Benjamin Grinstein, Grand Unified Theory with a Stable Proton, Int. J. Mod. Phys. A 33 (2018) 1844013 (arXiv:1808.00953)
Claim that threshold corrections can considerably alter (decrease) proton decay rate predictions in non-supersymmetric GUTs:
- Joydeep Chakrabortty, Stephen F. King, Rinku Maji, Unification, Proton Decay and Topological Defects in non-SUSY GUTs with Thresholds (arXiv:1901.05867)
Realistic models and phenomenology
Discussion of phenomenologically viable GUT-models (compatible with experiment and the standard model of particle physics):
-GUT
More on the original -approach:
- Ilja Doršner, Towards a minimal model arXiv:2206.06036
On quasi-realistic “flipped” -GUT, modeled in 4d heterotic string theory and subsuming realistic Starobinsky-type cosmic inflation:
-
Ignatios Antoniadis, John Ellis, John S. Hagelin, Dimitri Nanopoulos, The flipped string model revamped, Physics Letters B 231 1–2 (1989) 65-74 [doi:10.1016/0370-2693(89)90115-9]
-
Ignatios Antoniadis, Dimitri Nanopoulos, John Rizos, Cosmology of the string derived flipped , J. Cosm. Astrop. Phys 03 (2021) 017 [arXiv:2011.09396, doi:10.1088/1475-7516/2021/03/017]
-
Ignatios Antoniadis, Dimitri Nanopoulos, John Rizos, Particle physics and cosmology of the string derived no-scale flipped , Eur. Phys. J. C 82 (2022) 377 [arXiv:2112.01211, doi:10.1140/epjc/s10052-022-10353-6]
-GUT
The idea of “SO(10)” (Spin(10)) GUT originates with
- Harald Fritzsch, Peter Minkowski, Unified interactions of leptons and hadrons, Annals of Physics Volume 93, Issues 1–2, 5 September 1975, Pages 193-266 (doi:10.1016/0003-4916(75)90211-0)
Review:
-
Michal Malinský, 35 years of GUTs - where do we stand?, 2009 (pdf)
-
Stefano Bertolini, Luca Di Luzio, Michal Malinský, Intermediate mass scales in the non-supersymmetric SO(10) grand unification: a reappraisal, Phys. Rev. D80:015013, 2009 (arXiv:0903.4049)
for non-superymmetric models:
-
L. Lavoura and Lincoln Wolfenstein, Resuscitation of minimal grand unification, Phys. Rev. D 48, 264 (doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.48.264)
-
Guido Altarelli, Davide Meloni, A non Supersymmetric SO(10) Grand Unified Model for All the Physics below (arXiv:1305.1001)
-
Alexander Dueck, Werner Rodejohann, Fits to Grand Unified Models (arXiv:1306.4468)
-
Chee Sheng Fong, Davide Meloni, Aurora Meroni, Enrico Nardi, Leptogenesis in (arXiv:1412.4776)
(in view of leptogenesis)
-
Tommy Ohlsson, Marcus Pernow, Fits to Non-Supersymmetric SO(10) Models with Type I and II Seesaw Mechanisms Using Renormalization Group Evolution (arXiv:1903.08241)
-
Mainak Chakraborty, M.K. Parida, Biswonath Sahoo, Triplet Leptogenesis, Type-II Seesaw Dominance, Intrinsic Dark Matter, Vacuum Stability and Proton Decay in Minimal SO(10) Breakings (arXiv:1906.05601)
Results indicating non-SUSY as self sufficient theory for neutrino masses, baryon asymmetry, dark matter, vacuum stability of SM scalar potential, origin of three gauge forces, and observed proton stability.
-
Nobuchika Okada, Digesh Raut, Qaisar Shafi, Inflation, Proton Decay, and Higgs-Portal Dark Matter in (arXiv:1906.06869)
-
V. Suryanarayana Mummidi, Ketan M. Patel, Leptogenesis and fermion mass fit in a renormalizable model (arXiv:2109.04050)
-
George Lazarides, Rinku Maji, Rishav Roshan, Qaisar Shafi, A Predictive Model [arXiv:2210.03710]
with possible relation to flavour anomalies:
- Purushottam Sahu, Aishwarya Bhatta, Rukmani Mohanta, Shivaramakrishna Singirala, Sudhanwa Patra, Flavour anomalies and dark matter assisted unification in GUT [arXiv:2204.06392]
for supersymmetric models:
-
Archana Anandakrishnan, B. Charles Bryant, Stuart Raby, LHC Phenomenology of Models with Yukawa Unification II (arXiv:1404.5628)
-
Ila Garg, New minimal supersymmetric GUT phenomenology and its cosmological implications (arXiv:1506.05204)
On the symmetry breaking from Spin(10) to the standard model gauge group in terms of real normed division algebras (octonions, quaternions):
-
Kirill Krasnov, Geometry of Symmetry Breaking [arXiv:2209.05088]
-
Nichol Furey, M. J. Hughes, Division algebraic symmetry breaking [arXiv:2210.10126]
-GUT
Discussion for Spin(11) GUT group (“SO(11)”):
-
Yutaka Hosotani, Naoki Yamatsu, Gauge–Higgs grand unification, Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics, Volume 2015, Issue 11, November 2015 (doi:10.1093/ptep/ptv153, doi:10.1093/ptep/ptw116)
-
Atsushi Furui, Yutaka Hosotani, Naoki Yamatsu, Toward Realistic Gauge-Higgs Grand Unification, Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics, Volume 2016, Issue 9, September 2016, 093B01 (arXiv:1606.07222)
-
Yutaka Hosotani, Gauge-Higgs EW and Grand Unification, International Journal of Modern Physics AVol. 31, No. 20n21, 1630031 (2016) (arXiv:1606.08108)
-
Yutaka Hosotani, New dimensions from gauge-Higgs unification (arXiv:1702.08161)
-
Yutaka Hosotani, Naoki Yamatsu, Electroweak Symmetry Breaking and Mass Spectra in Six-Dimensional Gauge-Higgs Grand Unification (arXiv:1710.04811)
-GUT
Discussion for Spin(12) GUT group (“SO(12)”):
-
S. Rajpoot and P. Sithikong, Implications of the gauge symmetry for grand unification, Phys. Rev. D 23, 1649 (1981) (doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.23.1649)
-
Takaaki Nomura, Joe Sato, Standard(-like) Model from an Grand Unified Theory in six-dimensions with extra-space, Nucl.Phys.B811:109-122, 2009 (arXiv:0810.0898)
-
Takaaki Nomura, Physics beyond the standard model with extra-space, 2009 (pdf, pdf)
-
Cheng-Wei Chiang, Takaaki Nomura, Joe Sato, Gauge-Higgs unification models in six dimensions with extra space and GUT gauge symmetry (arXiv:1109.5835)
- and -GUT
Discussion for Spin(16) and Spin(18)? GUT group (“SO(16)” and “SO(18)?”):
-
Frank Wilczek, Anthony Zee, Families from spinors, Phys. Rev. D 25, 553 (1982) (doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.25.55310.1103/PhysRevD.25.553)
-
Goran Senjanović, Frank Wilczek, Anthony Zee, Reflections on mirror fermions, Physics Letters B Volume 141, Issues 5–6, 5 July 1984, Pages 389-394 Physics Letters B (doi:10.1016/0370-2693(84)90269-7)
-
Homero Martínez, Alejandra Melfo, Fabrizio Nesti, Goran Senjanović, Three Extra Mirror or Sequential Families: a Case for Heavy Higgs and Inert Doublet, Phys. Rev. Lett.106:191802, 2011 (arXiv:1101.3796)
-
Michael McGuigan, Dark Horse, Dark Matter: Revisiting the Nonsupersymmetric Model in the LHC and Dark Energy Era (arXiv:1907.01944)
-GUT
See at heterotic string – phenomenology
See also:
-
Alfredo Aranda, Francisco J. de Anda, Stephen F. King, Exceptional Unification of Families and Forces (arXiv:2005.03048)
-
Alfredo Aranda, Francisco J. de Anda, Complete Unification in 10 Dimensions (arXiv:2007.13248)
-
George Manolakos, Gregory Patellis, George Zoupanos, trinification from dimensional reduction of , 10D over and its phenomenological consequences (arXiv:2009.07059)
-
Francisco J. de Anda, Alfredo Aranda, António P. Morais, Roman Pasechnik, Gauge couplings evolution from the Standard Model, through Pati-Salam theory, into unification of families and forces (arXiv:2011.13902)
-
Alfredo Aranda, Francisco J. de Anda, António P. Morais, Roman Pasechnik, A Different Take on Unification (arXiv:2107.05421)
-
Alfredo Aranda, Francisco J. de Anda, António P. Morais, Roman Pasechnik, Sculpting the Standard Model from low-scale Gauge-Higgs-Matter Grand Unification in ten dimensions (arXiv:2107.05495)
-GUT
See at – Standard model phenomenology
Heterotic string phenomenology
The historical origin of all string phenomenology is the top-down GUT-model building in heterotic string theory due to
- Philip Candelas, Gary Horowitz, Andrew Strominger, Edward Witten, Vacuum configurations for superstrings, Nuclear Physics B Volume 258, 1985, Pages 46-74 Nucl. Phys. B 258, 46 (1985) [doi:10.1016/0550-3213(85)90602-9]
Review and exposition:
-
Edward Witten, Quest For Unification, Heinrich Hertz lecture at SUSY 2002 at DESY, Hamburg [arXiv:hep-ph/0207124]
-
Hans-Peter Nilles, Strings, Exceptional Groups and Grand Unification, talk at Planck 2011 [pdf, pdf]
-
Saul Ramos-Sanchez, Michael Ratz, Heterotic Orbifold Models, in Handbook of Quantum Gravity, Springer (2024) [doi:10.1007/978-981-19-3079-9,
Database of heterotic string vacua via stable vector bundles on Calabi-Yau 3-folds:
- Maxime Gabella, Yang-Hui He, Andre Lukas: An Abundance of Heterotic Vacua, Journal of High Energy Physics, 2008 JHEP12 (2008) [doi:10.1088/1126-6708/2008/12/027, arXiv:0808.2142]
The -heterotic string
The following articles claim the existence of exact realization of the gauge group and matter-content of the MSSM in heterotic string theory on orbifolds (not yet checking Yukawa couplings):
-
Volker Braun, Yang-Hui He, Burt Ovrut, Tony Pantev, A Heterotic Standard Model, Phys. Lett. B618 : 252-258 2005 (arXiv:hep-th/0501070)
-
Wilfried Buchmuller, Koichi Hamaguchi, Oleg Lebedev, Michael Ratz, Supersymmetric Standard Model from the Heterotic String, Phys. Rev. Lett. 96 121602 (2006) ([doi:varXiv:hep-ph/0511035]
-
Volker Braun, Yang-Hui He, Burt Ovrut, Tony Pantev, The Exact MSSM Spectrum from String Theory, JHEP 0605:043, 2006 (arXiv:hep-th/0512177)
-
Vincent Bouchard, Ron Donagi, An SU(5) Heterotic Standard Model, Phys. Lett. B633:783-791,2006 (arXiv:hep-th/0512149)
A computer search through the “landscape” of Calabi-Yau varieties showed severeal hundreds more such exact heterotic standard models (about one billionth of all CYs searched, and most of them arising as SU(5)-GUTs):
general computational theory:
- Lara Anderson, Yang-Hui He, Andre Lukas, Heterotic Compactification, An Algorithmic Approach, JHEP 0707:049, 2007 (arXiv:hep-th/0702210)
using heterotic line bundle models:
-
Lara Anderson, James Gray, Andre Lukas, Eran Palti, Two Hundred Heterotic Standard Models on Smooth Calabi-Yau Threefolds, Phys. Rev. D 84, 106005 (2011) (arXiv:1106.4804)
-
Lara Anderson, James Gray, Andre Lukas, Eran Palti, Heterotic Line Bundle Standard Models JHEP06(2012)113 (arXiv:1202.1757)
-
Lara Anderson, Andrei Constantin, James Gray, Andre Lukas, Eran Palti, A Comprehensive Scan for Heterotic GUT models, JHEP01(2014)047 (arXiv:1307.4787)
-
Yang-Hui He, Seung-Joo Lee, Andre Lukas, Chuang Sun, Heterotic Model Building: 16 Special Manifolds, J. High Energ. Phys. 2014, 77 (2014) (arXiv:1309.0223)
-
Stefan Groot Nibbelink, Orestis Loukas, Fabian Ruehle, Patrick K.S. Vaudrevange, Infinite number of MSSMs from heterotic line bundles?, Phys. Rev. D 92, 046002 (2015) (arXiv:1506.00879)
-
Andreas Braun, Callum R. Brodie, Andre Lukas, Heterotic Line Bundle Models on Elliptically Fibered Calabi-Yau Three-folds, JHEP04 (2018) 087 (arXiv:1706.07688)
-
Andrei Constantin, Yang-Hui He, Andre Lukas, Counting String Theory Standard Models, Physics Letters B
Volume 792, 10 May 2019, Pages 258-262 (arXiv:1810.00444)
-
Alon E. Faraggi, Glyn Harries, Benjamin Percival, John Rizos, Towards machine learning in the classification of orbifold compactifications (arXiv:1901.04448)
-
Magdalena Larfors, Robin Schneider, Explore and Exploit with Heterotic Line Bundle Models, Fortschritte der Physik Vol 86 Nr. 5 (arXiv:2003.04817)
The resulting database of heterotic line bundle models is here:
- Lara Anderson, James Gray, Andre Lukas, Eran Palti, Heterotic standard model database (web)
Review includes
-
Lara Anderson, New aspects of heterotic geometry and phenomenology, talk at Strings2012, Munich 2012 (pdf)
-
Yang-Hui He, Deep-learning the landscape, talk at String and M-Theory: The new geometry of the 21st century (pdf slides, video recording)
-
Yang-Hui He, Calabi-Yau Spaces in the String Landscape (arXiv:2006.16623)
Computation of metrics on these Calabi-Yau compactifications (eventually needed for computing their induced Yukawa couplings) is started in
- Volker Braun, Tamaz Brelidze, Michael Douglas, Burt Ovrut, Calabi-Yau Metrics for Quotients and Complete Intersections, JHEP 0805:080, 2008 (arXiv:0712.3563)
and via machine learning:
-
Andrei Constantin, Cristofero S. Fraser-Taliente, Thomas R. Harvey, Andre Lukas, Burt Ovrut, Computation of Quark Masses from String Theory [arXiv:2402.01615]
-
Per Berglund, Giorgi Butbaia, Tristan Hübsch, Vishnu Jejjala, Damián Mayorga Peña, Challenger Mishra, Justin Tan: Precision String Phenomenology [arXiv:2407.13836]
This “heterotic standard model” has a “hidden sector” copy of the actual standard model, more details of which are discussed here:
- Volker Braun, Yang-Hui He, Burt Ovrut, Supersymmetric Hidden Sectors for Heterotic Standard Models (arXiv:1301.6767)
The issue of moduli stabilization in these kinds of models is discussed in
-
Michele Cicoli, Senarath de Alwis, Alexander Westphal, Heterotic Moduli Stabilization (arXiv:1304.1809)
-
Lara Anderson, James Gray, Andre Lukas, Burt Ovrut, Vacuum Varieties, Holomorphic Bundles and Complex Structure Stabilization in Heterotic Theories (arXiv:1304.2704)
Principles singling out heterotic models with three generations of fundamental particles are discussed in:
- Philip Candelas, Xenia de la Ossa, Yang-Hui He, Balazs Szendroi, Triadophilia: A Special Corner in the Landscape, Adv.Theor.Math.Phys.12:2,2008 (arXiv:0706.3134)
Discussion of non-supersymmetric: GUT models:
- Alon E. Faraggi, Viktor G. Matyas, Benjamin Percival, Classification of Non-Supersymmetric Pati-Salam Heterotic String Models (arXiv:2011.04113)
See also:
- Carlo Angelantonj, Ioannis Florakis, GUT Scale Unification in Heterotic Strings, Physics Letters B 789 (2019) 496-501 [doi:10.1016/j.physletb.2018.12.054arXiv:1812.06915]
The -heterotic string
Discussion of string phenomenology for the SemiSpin(32)-heterotic string (see also at type I phenomenology):
-
Kang-Sin Choi, Stefan Groot Nibbelink, Michele Trapletti, Heterotic model building in four dimensions, JHEP 0412:063, 2004 (arXiv:hep-th/0410232)
-
Hans-Peter Nilles, Saul Ramos-Sanchez, Patrick K.S. Vaudrevange, Akin Wingerter, Exploring the Heterotic String, JHEP 0604:050 (2006) [doi:10.1088/1126-6708/2006/04/050arXiv:hep-th/0603086]
-
Saul Ramos-Sanchez, Towards Low Energy Physics from the Heterotic String, Fortsch. Phys. 10 (2009) 907-1036 [doi:10.1002/prop.200900073arXiv:0812.3560]
-
Naoki Yamatsu, String-Inspired Special Grand Unification, Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics, Volume 2017, Issue 10, 1 (arXiv:1708.02078, doi:10.1093/ptep/ptx135)
-
Jihn E. Kim, Grand unfication models from heterotic string (arXov:2008.00367)
On heterotic line bundle models:
- Hajime Otsuka, heterotic line bundle models, (arXiv:1801.03684)
The “”-heterotic string
This non-supersymmetric string theory was first described in:
-
Luis Alvarez-Gaumé, Paul Ginsparg, Gregory Moore and Cumrun Vafa, An heterotic string, Phys. Lett. B 171 (1986) 155 [doi:10.1016/0370-2693(86)91524-8]
-
Lance Dixon and Jeffrey Harvey, String Theories in Ten-Dimensions Without Space-Time Supersymmetry, Nucl. Phys. B 274 (1986) 93 [doi:10.1016/0550-3213(86)90619-X]
A proposal on what the correct global character of the gauge group is appears in:
- Brett McInnes, The Semispin Groups in String Theory, J. Math. Phys. 40 (1999) 4699-4712 [arXiv:hep-th/9906059, doi:10.1063/1.532999]
A suggestion that the heterotic string is a the string “minus” the semispin group :
- Adrian Norbert Schellekens, and Nicholas Warner Anomalies, characters and strings, Nuclear Physics B 287 (1987) 317-361 [doi:10.1016/0550-3213(87)90108-8]
In type II string theory
Computer scan of Gepner model-compactifications in relation to GUT-models is in
-
T.P.T. Dijkstra, L. R. Huiszoon, Bert Schellekens, Chiral Supersymmetric Standard Model Spectra from Orientifolds of Gepner Models, Phys.Lett. B609 (2005) 408-417 (arXiv:hep-th/0403196)
-
T.P.T. Dijkstra, L. R. Huiszoon, Bert Schellekens, Supersymmetric Standard Model Spectra from RCFT orientifolds, Nucl.Phys.B710:3-57,2005 (arXiv:hep-th/0411129)
Realization of GUTs in the context of M-theory on G2-manifolds and possible resolution of the doublet-triplet splitting problem is discussed in
-
Edward Witten, Deconstruction, Holonomy, and Doublet-Triplet Splitting, (arXiv:hep-ph/0201018)
-
Bobby Acharya, Krzysztof Bozek, Miguel Crispim Romao, Stephen F. King, Chakrit Pongkitivanichkul, Grand Unification in M theory on a manifold (arXiv:1502.01727)
Discussion of GUTs in F-theory includes
-
Chris Beasley, Jonathan Heckman, Cumrun Vafa, GUTs and Exceptional Branes in F-theory - I (arxiv:0802.3391), II: Experimental Predictions (arxiv:0806.0102)
-
Chris Beasley, Jonathan Heckman, Cumrun Vafa, GUTs and Exceptional Branes in F-theory - I, JHEP 0901:058,2009 (arXiv:0802.3391)
-
Gianluca Zoccarato, Yukawa couplings at the point of in F-theory, 2014 (pdf/zoccarato.pdf))
-
Cumrun Vafa, Reflections on F-theory, 2015 (pdf)
In Connes-Lott models
Discussion of GUTs within Connes-Lott models:
-
Ali Chamseddine, Alain Connes, Viatcheslav Mukhanov, Quanta of Geometry: Noncommutative Aspects, Phys. Rev. Lett. 114 (2015) 9, 091302 (arXiv:1409.2471)
-
Ali Chamseddine, Alain Connes, Viatcheslav Mukhanov, Geometry and the Quantum: Basics, JHEP 12 (2014) 098 (arXiv:1411.0977)
-
Alain Connes, section 4 of Geometry and the Quantum, in Foundations of Mathematics and Physics One Century After Hilbert, Springer 2018. 159-196 (arXiv:1703.02470, doi:10.1007/978-3-319-64813-2)
Exotica: Leptoquarks, -bosons, etc.
Topological defects can play considerable role to constrain the non-SUSY and SUSY GUTs:
- Joydeep Chakrabortty, Rinku Maji, Sunando Kumar Patra, Tripurari Srivastava, Subhendra Mohanty, Roadmap of left-right models based on GUTs (arXiv:1711.11391, Phys.Rev. D97 (2018) no.9, 095010.)
Relation to Z'-bosons:
- S. Sahoo, The prediction of mass of -boson in an -based model, Indian J. Phys. 80 (2), 191-194 (2006) (pdf)
Relation to leptoquarks and flavour anomalies:
-
H. Murayama, T. Yanagida, A viable GUT with light leptoquark bosons, Mod.Phys.Lett. A7 (1992) 147-152 (arXiv:315898, doi:10.1142/S0217732392000070)
-
Damir Bečirević, Ilja Doršner, Svjetlana Fajfer, Nejc Košnik, Darius A. Faroughy, Olcyr Sumensari, Scalar leptoquarks from GUT to accommodate the -physics anomalies, Phys. Rev. D 98, 055003 (2018) (arXiv:1806.05689)
-
Ufuk Aydemir, Tanumoy Mandal, Subhadip Mitra, A single TeV-scale scalar leptoquark in SO(10) grand unification and B-decay anomalies (arXiv:1902.08108)
-
Julian Heeck, Daniele Teresi, Pati-Salam explanations of the B-meson anomalies, JHEP 12 (2018) 103 (arXiv:1808.07492)
-
Julian Heeck, Daniele Teresi, Pati-Salam and lepton universality in B decays (arXiv:1905.05211)
-
Michal Malinský, Lepton non-universality in -decays in the minimal leptoquark gauge model (arXiv:1906.09174)
-
Shyam Balaji, Michael A. Schmidt, A unified theory for the and anomalies (arXiv:1911.08873)
Modeled on branes:
- Javier Fuentes-Martin, Gino Isidori, Julie Pagès, Ben A. Stefanek,
Flavor Non-universal Pati-Salam Unification and Neutrino Masses, Physics Letters B Volume 820, 10 September 2021, 136484 (arXiv:2012.10492, talk recording)
Last revised on July 10, 2025 at 12:20:15. See the history of this page for a list of all contributions to it.